Introduction to Kubernetes Deployment¶
A Kubernetes Deployment tells Kubernetes how to create or modify instances of the pods.
You describe a desired state in a Deployment, and the Deployment Controller changes the actual state to the desired state at a controlled rate.
Using Deployments you can easily scale the number of replica pods, enable the rollout of updated code in a controlled manner, or roll back to an earlier deployment version if necessary.
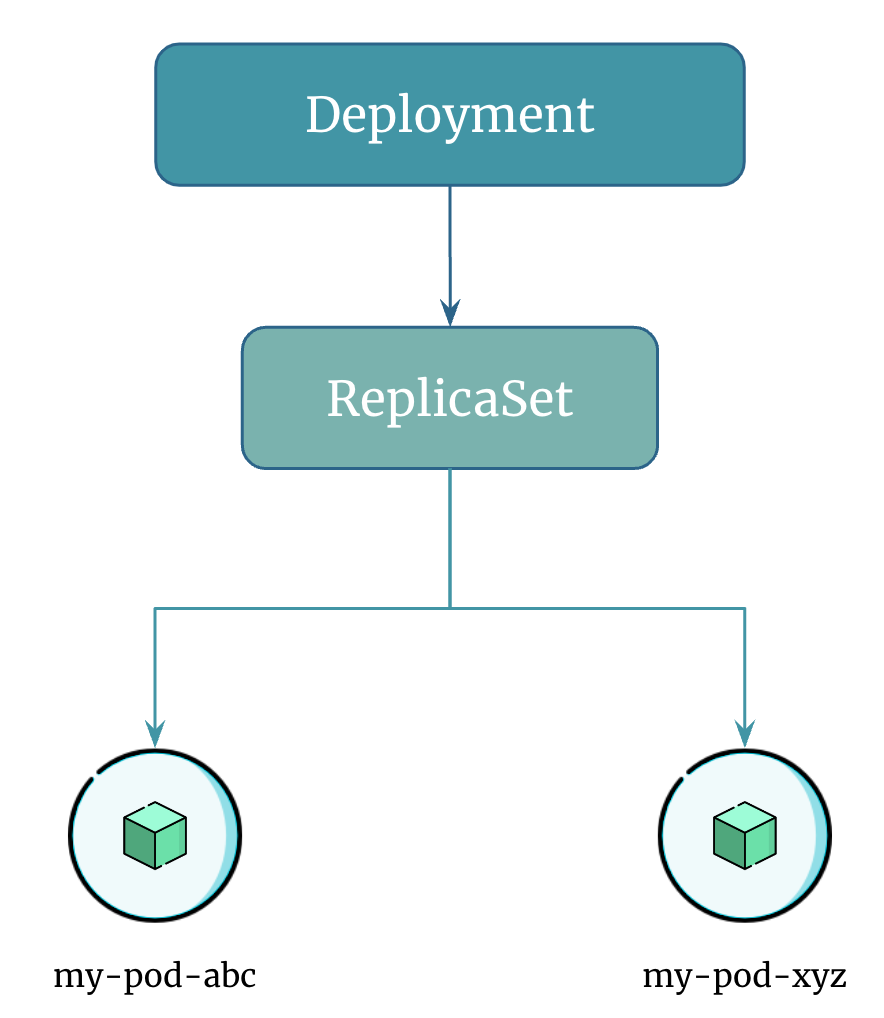
Deployment in Kubernetes is an abstraction of a ReplicaSet. When you create a Deployment, Kubernetes creates a ReplicaSet for you and manages the replicas of your application based on the Deployment's desired state.
Deployments provide additional features such as rolling updates, rollbacks, and scaling strategies, which are not available with ReplicaSets alone.
Deployment Overview¶
Deployment doesn't interact with pods directly. It manages pods using ReplicaSets.
Deployment does the rolling update automatically without any human interaction and increases the abstraction by one level.
It is recommended to use Deployments instead of directly using ReplicaSets, unless you require custom update orchestration or don't require updates at all.