Rollback a Kubernetes Deployment¶
In Kubernetes, a rollback is the process of reverting a Deployment to a previous revision.
When you update a Deployment, Kubernetes stores the previous revision(s) of the Deployment's configuration and the ReplicaSets it created.
If there is an issue with the new revision, you can use the kubectl rollout undo command to rollback to a particular revision.
Step 1: Rollback to Previous Revision¶
# Command template
kubectl rollout undo deployment <deployment-name>
{OR}
kubectl rollout undo deployment/<deployment-name>
# Actual command
kubectl rollout undo deployment my-deployment
{OR}
kubectl rollout undo deployment/my-deployment
Verify rollback:
Step 2: Rollback to a Particular Revision¶
To rollback a Kubernetes Deployment to a particular version, You can use the kubectl rollout undo command with the --to-revision flag followed by the revision number:
# Command template
kubectl rollout undo deployment <deployment-name> --to-revision=<revision-number>
{OR}
kubectl rollout undo deployment/<deployment-name> --to-revision=<revision-number>
# Actual command
kubectl rollout undo deployment my-deployment --to-revision=1
{OR}
kubectl rollout undo deployment/my-deployment --to-revision=1
Verify rollback:
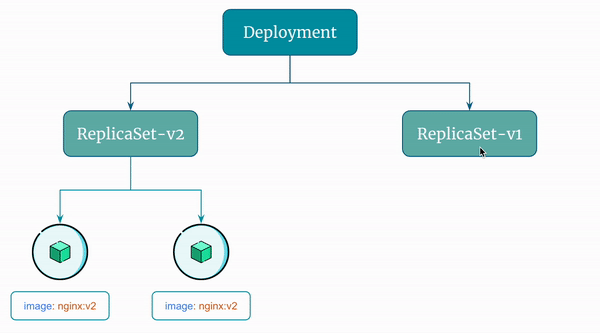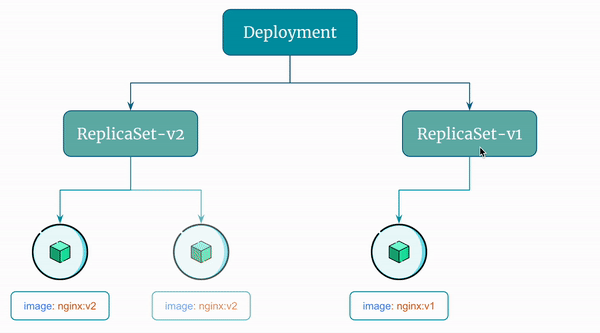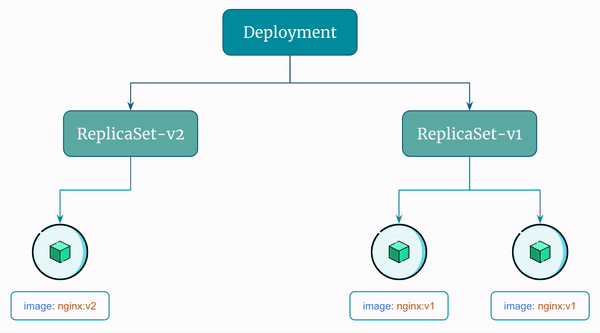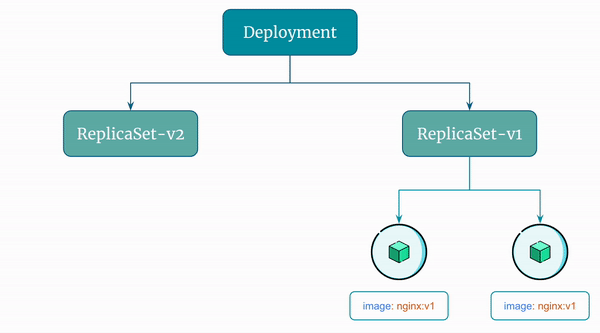
Here's a visual representation of the rollback the Deployment performs:
Clean Up¶
Delete the Deployment: