Update a Kubernetes Deployment¶
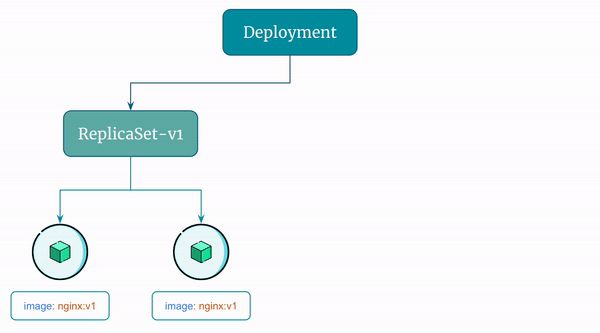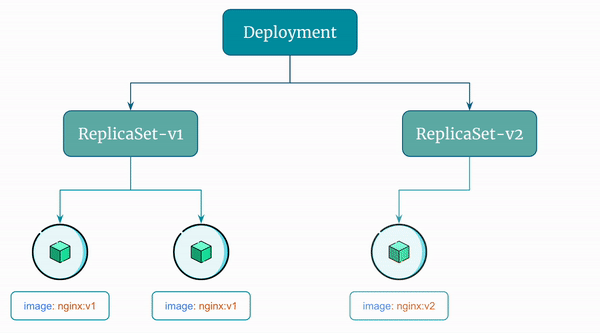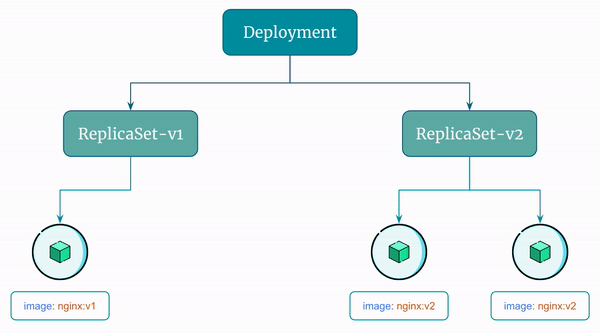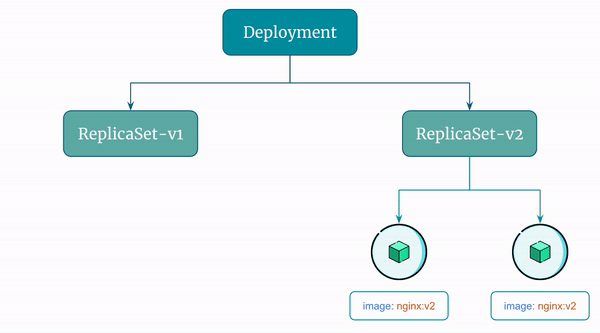
By default, Kubernetes performs rolling updates when you update a Deployment. It does so by creating a new ReplicaSet.
The old ReplicaSets are not deleted. By default, Kubernetes Deployment controller stores up to 10 revisions of a Deployment. This means that when you update a Deployment, the controller will keep up to 10 previous versions of the Deployment's configuration and the ReplicaSets it created.
Let's see this in action!
Step 1: Update a Deployment¶
Let's update the Deployment to use a new image reyanshkharga/nginx:v2.
You can use kubectl set image command to update the Deployment to use a new image.
# Command template
kubectl set image deployment <deployment-name> <container-name>=<new-image>
{OR}
kubectl set image deployment/<deployment-name> <container-name>=<new-image>
# Actual command
kubectl set image deployment my-deployment nginx=reyanshkharga/nginx:v2
{OR}
kubectl set image deployment/my-deployment nginx=reyanshkharga/nginx:v2
Step 2: Verify if the Deployment Was Updated¶
Verfify the Deployment, Pods, and ReplicaSets:
# Describe deployment
kubectl describe deploy/my-deployment
# List pods
kubectl get pods | grep my-deployment
# List replicasets
kubectl get rs | grep my-deployment
You'll observe the following:
- The
Deploymentis updated and uses the updated image. - A new
ReplicaSetis created - New Pods come up and old Pods are terminated.
- Old
ReplicaSetsare not deleted (unless this was 11th revision)
Here's a visual representation of the rolling update the Deployment performs:
Step 3: List Deployment Revisions¶
As discussed earlier, Kubernetes Deployment controller stores up to 10 revisions of a Deployment.
You can configure the maximum number of revisions to keep by setting the .spec.revisionHistoryLimit field in the Deployment's YAML file using kubectl edit deployment command.
List the Deployment revisions:
# Command template
kubectl rollout history deployment <deployment-name>
{OR}
kubectl rollout history deployment/<deployment-name>
# Actual command
kubectl rollout history deployment my-deployment
{OR}
kubectl rollout history deployment/my-deployment
Get the details of a particular revision:
# Command template
kubectl rollout history deployment <deployment-name> --revision=<revision-number>
{OR}
kubectl rollout history deployment/<deployment-name> --revision=<revision-number>
# Actual command
kubectl rollout history deployment my-deployment --revision=2
{OR}
kubectl rollout history deployment/my-deployment --revision=2
List ReplicaSets managed by the Deployment: