Install Kiali¶
Kiali is an observability console for Istio with service mesh configuration and validation capabilities. It helps you understand the structure and health of your service mesh by monitoring traffic flow to infer the topology and report errors.
Step 1: Prepare YAML Manifest for Kiali¶
Copy samples/addons/kiali.yml manifest from Istio download package. We will make some modification to this file before deploying.
Edit the kiali.yml by adding grafana and prometheus url in the kiali configmap. It should look like the below:
external_services:
...
grafana:
enabled: true
in_cluster_url: http://grafana.grafana:80
url: https://grafana.example.com
prometheus:
url: http://prometheus-server.prometheus:80
jaegar:
url: http://tracing.istio-system:80
Step 2: Deploy the Manifest to Install Kiali¶
Let's apply the modified manifest to install Kiali:
Step 3: Access Kiali Dashboard Locally¶
Let's use kubectl port-forward to access Kiali dashboard locally:
# Check the port kiali is exposed at
kubectl get svc -n istio-system | grep kiali
# Forward port 20001 of kiali service on port 20001 of the local host machine
kubectl port-forward svc/kiali 20001:20001 -n istio-system
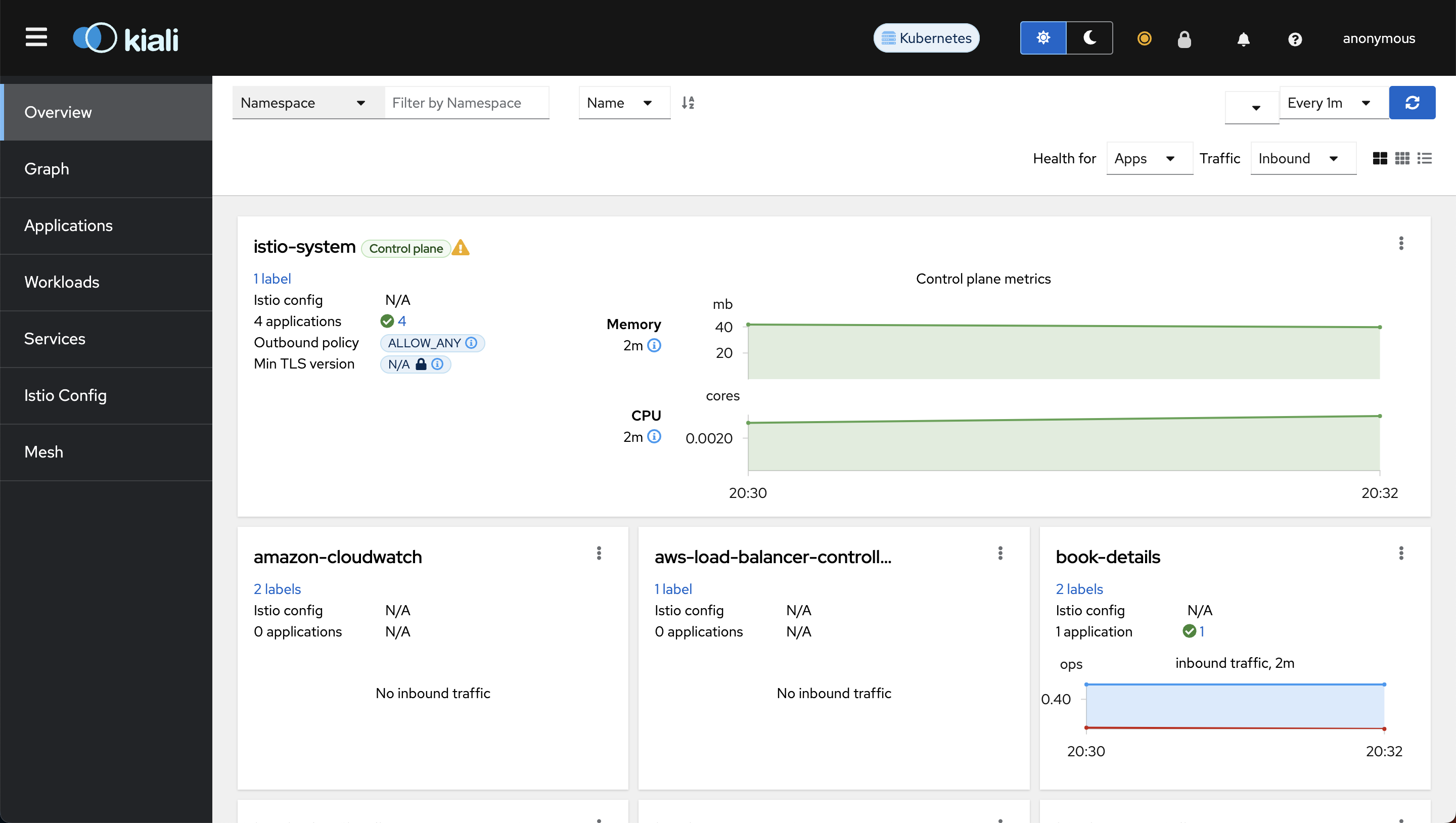
Open any browser on your local host machine and visit localhost:20001. You should see the Kiali dashboard.
Step 4: Deploy Ingress for Kiali¶
We'll use an ingress to access Kiali externally using a load balancer.
Apply the manifest to create ingress for Kiali:
Step 5: Verify Kiali Installation¶
Visit the Kiali host (kiali.example.com) to verify whether you can access the Kiali Dashboard and observe the interaction between microservices.
At this moment, the Kiali graph might seem unclear because we're currently utilizing kubernetes ingress for our microservices instead of the native gateway and virtual service in Istio. Once we update our microservices to use the Istio gateway and virtual service, you'll see a more accurate graph illustrating the interactions between our microservices.
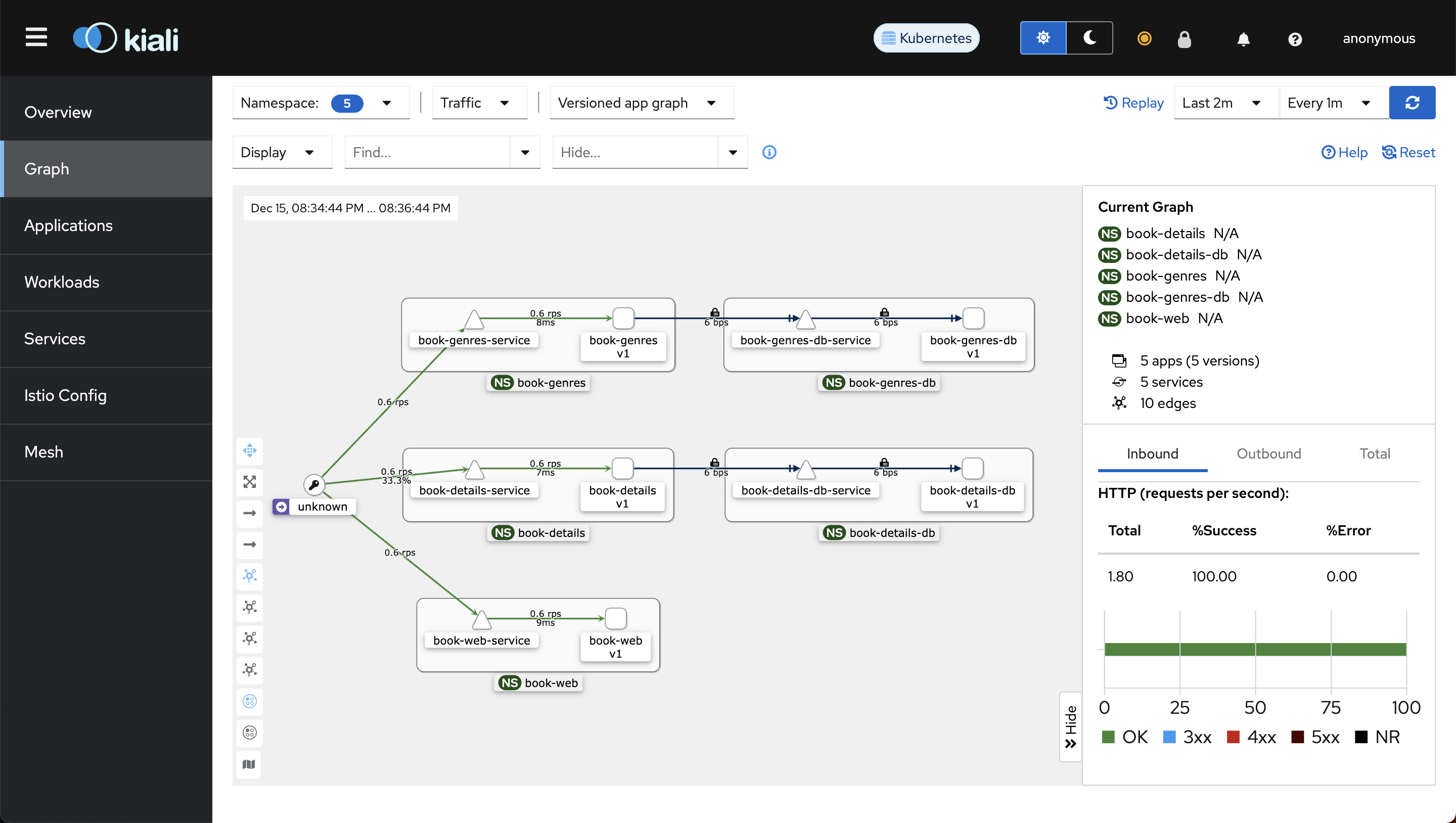
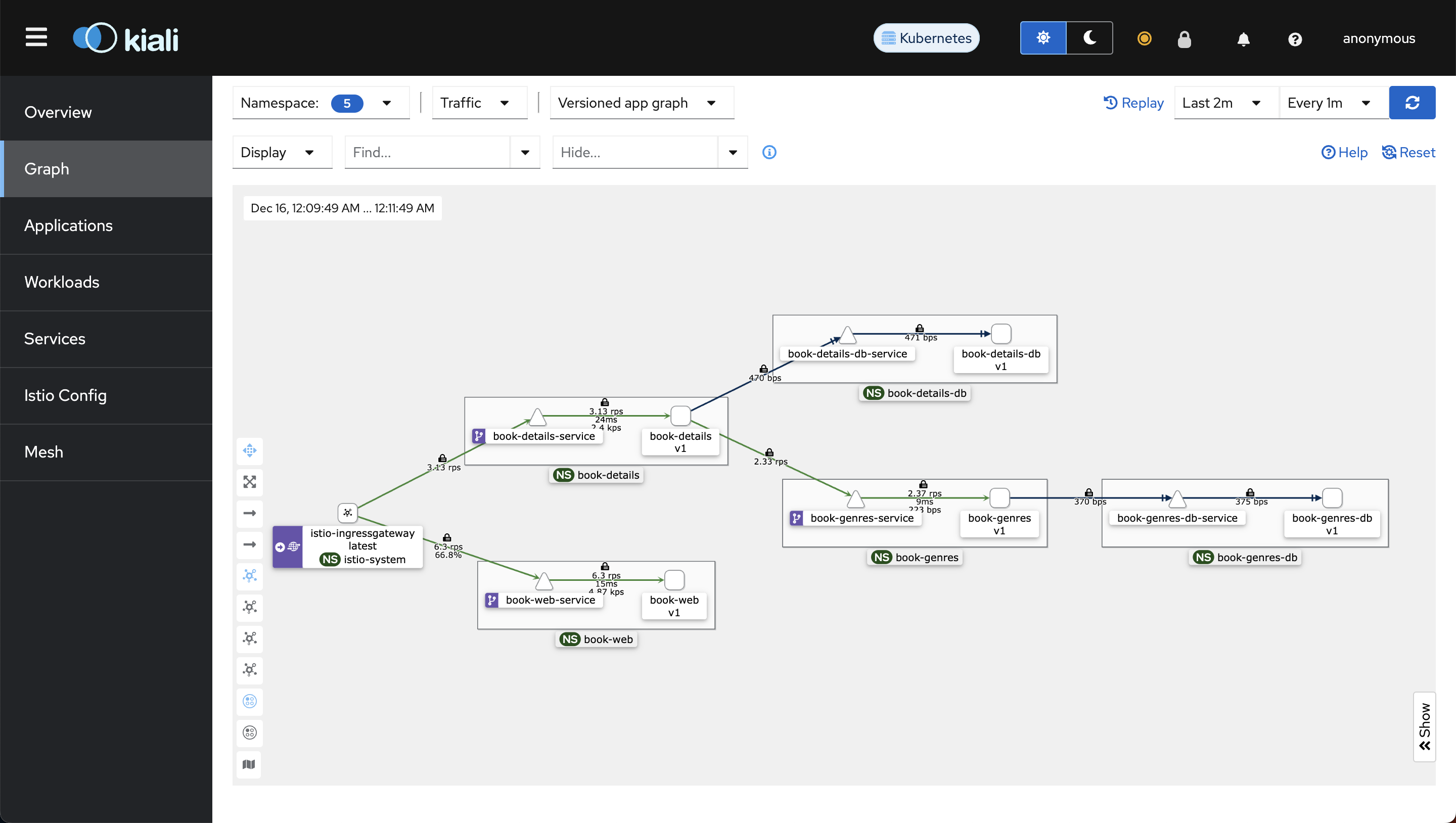
Here's a glimpse of how kiali service graph will look like when we update our microservices:
Notice how book-details-service calls book-genres-service and both services independently calls their respective databases.
You won't see book-web-service calling book-details-service in the graph because book-web-service uses the public API to call book-details-service.